Smart Health
In 2025, smart health technology is fundamentally transforming the way healthcare is delivered and experienced. Artificial intelligence breakthroughs, remote monitoring, wearables, and new generation technology in telemedicine are redefining the limits of medical care, making it more accessible, personalized, and proactive than it has ever been. Patients get immediate access to information about their health, and medical professionals have potent means to foresee the problems, personalize treatment, and improve outcomes.
This article explores the key technological trends that are defining the healthcare sector in this year and how they are influencing patients, professionals, and the future of care in general.
The Rise of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
2025 will see a major leap in the use of artificial intelligence (AI) across the healthcare systems. Artificial intelligence (AI) applications are not just used in diagnostic aid anymore: they are used to inform symptom checkers and virtual health assistants, to discover drugs based on data and robotics, and to automate hospital processes. An example is clinical AI tools, which analyze medical images effectively, identify diseases such as pneumonia or cancer faster than before, and assist clinicians in making correct and timely decisions.
Personalized medicine is also achieved with the help of AI, with the real-time patient data provided by wearables and monitoring devices guiding specific treatment plans that can be modified in real-time when fed with feedback and other needs. The predictive analytics developed based on machine learning models operate on very large volumes of patient data and help prevent adverse events.
Remote Monitoring and Wearable Devices
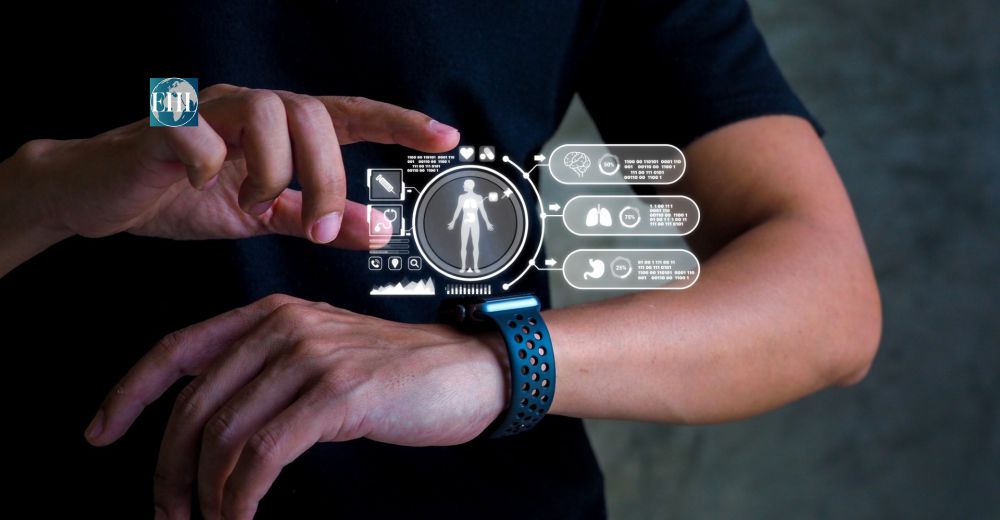
In 2025, healthcare access and delivery are still being redefined by remote patient monitoring, wearable health devices, and smart implants. Sensors are connected to patients with chronic conditions and can transmit real-time data to the clinician to inform about cardiac rhythm, glucose level, and physiological changes, and make immediate interventions, e.g., for heart failure.
Smartwatches and bracelets monitor essential health parameters, including sleep quality and activity rates, as well as vital signs, giving patients greater control over their health and helping to maintain constant clinician control over patients. Neural and cardiac implants are innovated, and 3D bioprinting and custom designing enhance the results in rehabilitation and the inability to cure some disabilities before.
Telemedicine and Virtual Care Become Standard
Telemedicine has become an essential part of the health ecosystem, and its main advantage is to enlarge access to patients in both urban and remote locations. Quality video calls and AI-enhanced online care systems permit a transparent interaction process, instant health evaluation, and quick responses from the provider. Remote robotic surgery is made possible through technologies like 5G, and it allows emergency responders to broaden their vital statistics in real-time, allowing hospitals to get ready before patients arrive.
Chatbots and other AI-based virtual health assistants have been deployed to help patients check symptoms, book appointments, take medication, and process administrative questions, making the process efficient and allowing clinicians to work directly with patients.
Robotics, Virtual Reality, and Augmented Education
The implementation of robotic surgery systems is no longer an imaginary concept, as trained surgeons remotely control precision tools and can conduct complex surgery with little to no latency due to the 5G development.
In the meantime, AR and VR headsets are used to improve medical training, allowing students and professionals to see complicated anatomy and simulate a procedure in a virtual world before using it in practice. Mixed reality and digital twin technologies also speed up the process of design and testing of new devices and treatments to offer safe and cost-effective pipelines of innovation in clinical research.
Challenges and Future Prospects
The main challenges of smart health technology in 2025 revolve around three areas, namely cybersecurity, AI bias and system integration.
Cybersecurity threats: The issue of cybersecurity threats is increasingly growing, and health facilities are frequent targets of ransomware attacks and have to pay outlandish amounts to guarantee the security of confidential patient data.
AI bias and transparency: AI bias and transparency are not fully eliminated so far; incomplete or biased data may give incorrect diagnoses or suggestions, and the companies may also need audits and clinical oversight.
Digital tool integration: The introduction of digital tool integration has not been offered with ease since the health data is not in different systems capable of minimizing the efficacy of workflow and slowing down the process of patient care coordination.
All these challenges require constant solutions in staff training, security, usability, and regulation in order to make sure that technology improves patient outcomes.
Conclusion
The future of patient care in 2025 will be transformed with more accessible, personalized, and proactive smart technology. The application of AI, IoT, and telemedicine can also provide better data and decision-making to patients and their providers. All these advantages can be achieved only when data protection, system compatibility, and responsible AI usage are appropriately cared for. The future of healthcare is in using these innovations without compromising patient well-being and clinical expertise.